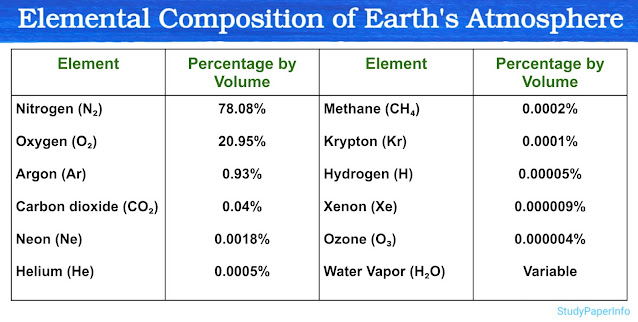
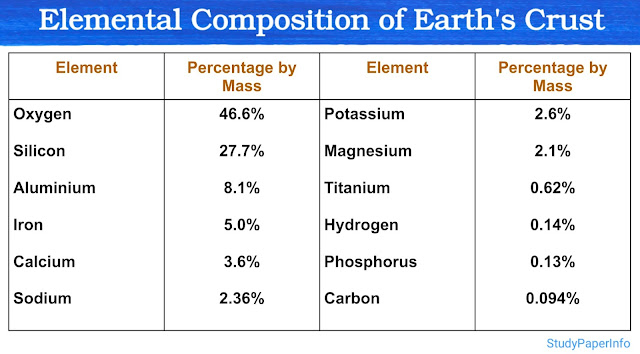
CSIR NET Life Science syllabus 2025
CSIR-UGC National Eligibility Test (NET) for Junior Research Fellowship and Lecturer-ship LIFE SCIENCES Molecules and their Interaction Relevant to Biology Cellular Organization Fundamental Processes Cell Communication and Cell Signaling Developmental Biology System Physiology – Plant System Physiology – Animal Inheritance Biology Diversity of Life Forms Ecological Principles Evolution and Behavior Applied Biology Methods in Biology 1. MOLECULES AND THEIR INTERACTION RELAVENT TO BIOLOGY A. Structure of atoms, molecules and chemical bonds. B. Composition, structure and function of biomolecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids and vitamins). C. Stablizing interactions (Van der Waals, electrostatic, hydrogen bonding, hydrophobic interaction, etc.). D Principles of biophysical chemistry (pH, buffer, reaction kinetics, thermodynamics, colligative properties). E. Bioenergetics, glycolysis, oxidative phosphorylation, coupled reaction, group transfer, biological ener...