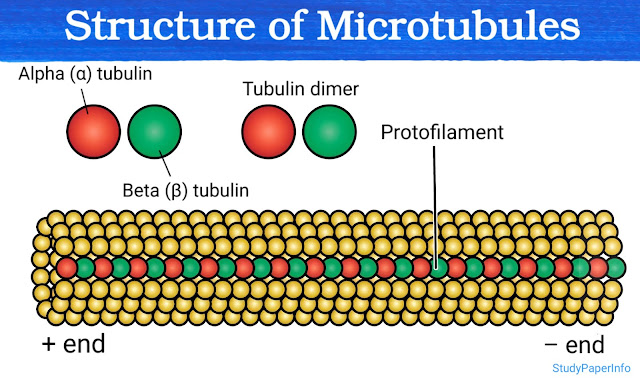
Explain why MTs have polar structures
Microtubules have polar structures because of the specific arrangement and asymmetric nature of their building blocks called tubulin heterodimers. Each heterodimer is made of two different protein subunits: α-tubulin (alpha tubulin) and β-tubulin (beta tubulin). These two are chemically and structurally different, so they cannot switch positions. They always stay in the same fixed orientation, with α-tubulin at one end and β-tubulin at the other. When these α/β-tubulin dimers come together to form microtubules, they arrange in a head-to-tail manner in one direction only. The β-tubulin of one dimer attaches to the α-tubulin of the next dimer and this pattern repeats again and again. Because of this straight, uniform and unidirectional arrangement, the microtubule has a distinct structure with two different ends. These two ends are called the plus end and the minus end, and they behave differently: Plus end (β-tubulin is exposed): This end is more ...