When a white cow was mated with a red bull, all their offspring were a mottled red and white (roan) colour. If the two roan cattle were mated, what coat colour would the progeny have and in what ratios
Question: When a white cow was mated with a red bull, all their offspring were a mottled red and white (roan) colour. If the two roan cattle were mated, what coat colour would the progeny have and in what ratios.
This question is based on codominance, where both alleles express themselves equally in the heterozygous state. In this case, red coat and white coat are codominant traits.
Genetic Symbols Used:
- R = Allele for red coat
- W = Allele for white coat
Since both alleles are codominant, heterozygous condition (RW) shows a roan coat, which is a mix of red and white patches.
Step 1: Initial Cross
- Parent 1 (Red bull) = RR
- Parent 2 (White cow) = WW
When RR is crossed with WW:
In F₁ Generation:
- All offspring: RW (heterozygous)
- Phenotype: Roan coat (both red and white patches visible)
Step 2: Cross Between Two Roan Cattle
Now we cross two Roan (RW × RW) individuals.
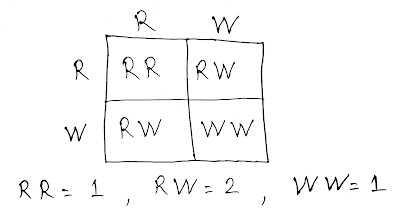
Let's draw a Punnett Square for the cross:
Step 3: Resulting Genotypes and Phenotypes
From the Punnett square, we get:
- 1 RR = Red coat
- 2 RW = Roan coat (Red + White patches)
- 1 WW = White coat
Final Phenotypic Ratio:
- 25% Red (RR)
- 50% Roan (RW)
- 25% White (WW)
Thus, when two roan cattle (RW × RW) are crossed, the offspring will show:
1 Red : 2 Roan : 1 White
This is the phenotypic ratio in codominant inheritance.

Comments
Post a Comment